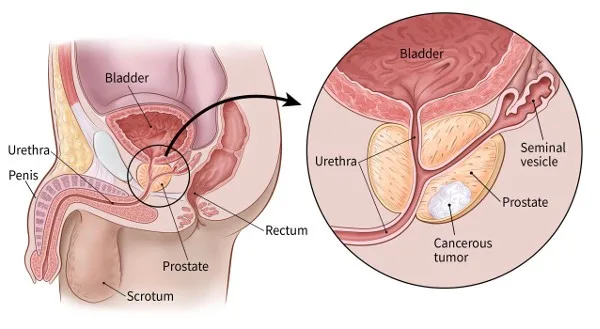
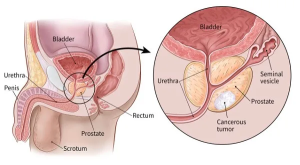
The prostate gland is a little gland that sits in front of the rectum and beneath the bladder. Generating seminal fluid, which feeds and moves the sperm, is its primary job. Prostate cancer, which will be covered in this article, is the most deadly illness that affects this gland.
According to a 2023 Nigerian study, prostate cancer is the most common cancer among Nigerian males. Previously thought to be a disease mostly affecting the elderly, over 8.86% of young Nigerian men have been diagnosed with the condition.
We are aware that June is Men’s Health Month, therefore in honour of this occasion, we will be discussing prostate cancer, its symptoms, risk factors, and preventive strategies.
Source: American Cancer Society
What is Prostate Cancer?
Located underneath the bladder in men, the prostate is a tiny, walnut-shaped gland. In the male reproductive system, the prostate gland is essential because it produces seminal fluid, which feeds and moves sperm.
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland develop improperly and reproduce uncontrollably. These cancer cells grow slowly most of the time and can go on for many years without symptoms. Prostate cancers can, nevertheless, occasionally become aggressive and spread to other body areas (lungs, bone, liver lymph nodes).
Although there are certain risk factors the exact cause of many cancers as well as prostate cancer is still largely unknown. Early detection remains key in the management of prostate cancer.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer risk can be raised by many variables, such as:
- Age: The risk is higher for men over 50.
- Family History: An increased risk is associated with a family history of prostate cancer.
- Ethnicity: African-Americans, Black, and African males, including those from Nigeria, are more likely to develop prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle and Nutrition: A diet heavy in red meat and poor in fruits and vegetables may put a person at risk. Obese and overweight men are at risk of advanced/metastatic prostatic cancer. Smokers have a higher-than-normal risk of having prostate cancer.
- Genetics: The risk may be raised by specific genetic mutations, inheriting the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes increases the risk.
Signs and symptoms of prostate cancer
Source: Gleneagles Hospital
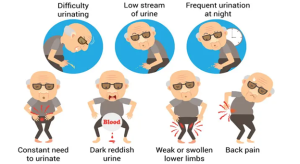
Most cases of early prostate cancer are symptomless and as such what prostate cancer may present as or look like is essential for you to know. Prostate cancer that has progressed may cause:
- weak urine stream or trouble peeing,
- frequent urination,
- blood in the semen or pee,
- pain or burning sensation during urination or ejaculation,
- discomfort in the hips, pelvis, or back, and
- impotence (erectile dysfunction).
Advanced prostate cancer have the below in addition to the above symptoms:
- Tiredness
- Bone pain
- Unexplained weight loss.
Prostate cancer treatment outcomes are considerably improved by early identification and early detection can provide a cure for men. For early detection to be possible, you must get regular screenings, particularly if you are over 50 or have a family history of prostate cancer. The two main techniques for screening are the blood and physical exam tests.
The PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test is the blood test that determines blood PSA levels, prostate cancer may be present if the levels are elevated while the Digital Rectal Exam(DRE) is a physical exam done in the clinics. The physician examines the prostate gland through the rectum for anomalies in the gland.
Prevention of Prostate Cancer
To lower your risk of prostate cancer, you can adopt the following proactive measures:
- Frequent Screenings: Men over 50 should have DREs and PSA testing frequently. It is vital if you have a family history of prostate cancer, as it is better to begin screening sooner.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Reducing risk can be achieved by eating a diet high in fruits and vegetables, keeping a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise. Additionally, reduction and cessation of smoking and alcohol can drastically reduce your risk of prostate cancer and other cancers that affect men.
- Open Communication: Be bold and voice your worries and ask inquiries regarding your health and that of your prostate.
- Early Detection: Seek immediate medical assistance if you suspect any symptoms.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer is relatively common and the fifth most common cause of death in men. Early identification of symptoms and detection through screening remains crucial. Regular screening is the greatest approach to finding prostate cancer in its early stages. People should start screening at age 40, depending on risk factors.
To discuss with licensed physicians and have a comprehensive cover for your general health, send us a WhatsApp message today!
Dr. Ifeoma M. Uduh, Dr John Afam