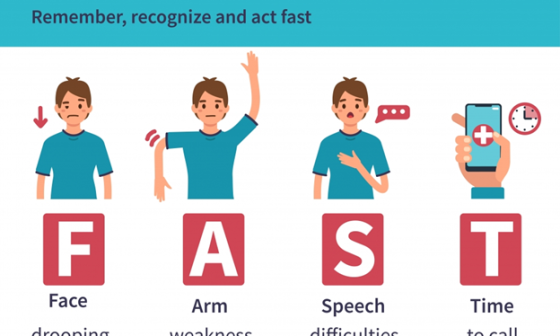
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic and endocrine disorder of a hormone called Insulin. It is a chronic illness that develops when the body either cannot use the insulin that the pancreas makes properly or the pancreas does not create enough of it.
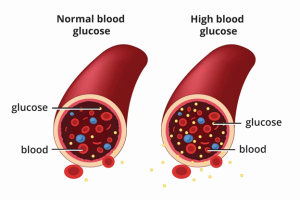
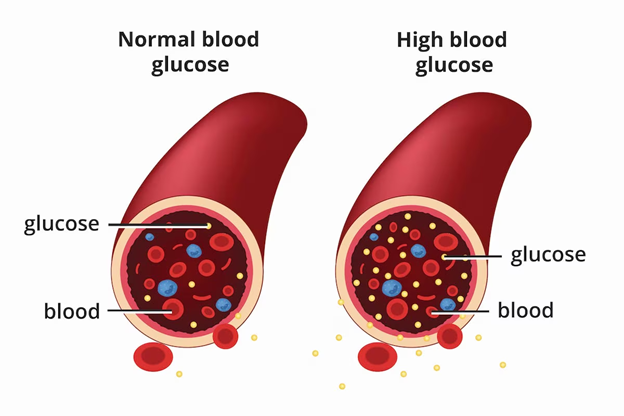
Source: National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Disease
One hormone that controls blood sugar in the body is insulin. Elevated blood glucose or elevated blood sugar, is a frequent consequence of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus that eventually causes major harm to numerous body and tissue systems, particularly the blood vessels and neurons (nerves) causing organ damage.
This article will explore the types, risk factors, signs, and management of diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Mellitus Types
Diabetes comes in three primary forms: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune (self-destruction) condition in which the body targets the pancreatic cells that produce insulin and destroys them. Insulin injections are a lifelong necessity for people with type 1 diabetes to control their blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
Health organizations like the WHO claim that about ninety per cent of all diabetes mellitus cases are of type 2, which makes it the most prevalent kind. In this type, the body either stops producing enough insulin or develops resistance to its effects. Although lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise are frequently the primary line of treatment, prescription drugs may also be required, in the long run, there may be a need for insulin in the management of this condition.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is also known as pregnancy diabetes. Pregnancy causes the development of gestational diabetes, which often goes away after delivery. However, type 2 diabetes is more likely to affect women who have gestational diabetes in the future.
Diabetes Risk Factors
The precise causes of diabetes are not entirely understood, several factors can raise one’s chance of getting the disease and these are called risk factors. Risk factors include ethnicity, bad diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, genetic risk, and high blood pressure.
- Weight: One of the main risk factors for type 2 diabetes is being overweight or obese.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Low or no levels of physical activity (sedentary lifestyle) raises the risk of having diabetes.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diabetes may be brought on by a diet heavy in processed foods, sugar-filled beverages, and unhealthy fats.
- Race & Ethnicity: People of particular races and ethnicities are more likely to get type 2 diabetes.
- Age: Research has shown that as people age, their risk of type 2 diabetes rises.
- Poor Habits: Smoking and alcoholism raise a person’s risk of developing diabetes mellitus.
- Medical Conditions: Hypertension, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), cardiovascular disease, pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer or tumours, etc. These conditions can predispose an individual to diabetes mellitus.
There are preventive strategies people can take to lower their chance of acquiring diabetes, even if some risk factors, like heredity, are unavoidable. These include controlling stress, eating a balanced diet, staying physically active regularly, abstaining from tobacco and alcohol, and keeping a healthy weight.
Identifying Diabetes Symptoms and Signs
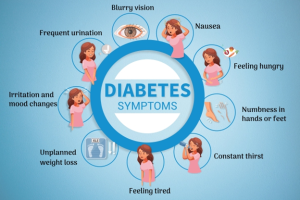
Source: Thyrocare Creator: DEEPAK BHARATI
Typical signs of diabetes include the following:
- Excessive urination and thirst,
- heightened appetite,
- unexpected weight loss,
- unexplained fatigue,
- hazy vision/ blurry vision,
- slow-healing injuries, and
- recurring infections.
To avoid complications, diabetes must be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible. If you notice any of the red flags, be tested by a medical practitioner. Wellahealth Technologies provides a medical cover that you and your family the opportunity to get tested for diabetes, we also offer telemedicine consultations when you subscribe to any of our plans.
Managing Diabetes
Treating diabetes calls for a diversified strategy that includes medication, dietary changes, and ongoing observation. To assist in controlling blood sugar levels, doctors may prescribe medications like insulin and oral hypoglycemic medicines. A balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins aids in the management of diabetes. However, frequent exercise is also essential for lowering the risk, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and managing weight.
Healthy food: Food that is balanced and full of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Minimizing sugar-filled beverages, processed foods, and harmful fats.
Regular activity: Getting at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-to-intense activity or 75 minutes a week of vigorous exercise.
Weight and stress management: Reducing weight can greatly enhance blood sugar regulation for overweight or obese people. Prolonged stress might exacerbate dysglycemia. Healthy stress-reduction strategies, like yoga or relaxation methods are necessary.
Medication: If required, prescription drugs should be taken exactly as directed by the physician.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular blood sugar levels are essential as well as making any necessary dietary, activity, or medication adjustments.
Regular Checkup: Routine visits with the physician to keep an eye on diabetes and general health are mandatory in the management of diabetes.
Conclusion
We’re here to help at Wellahealth because diabetes requires constant care, but you don’t have to handle it by yourself and the good news now is that you can reverse diabetes! We currently are running a Diabetes Reversal Clinic. Contact us on WhatsApp to know how you can do this and join our online community and support group(Meditrina).
With diabetes, you can lead a satisfying life if you have the right information, take preventive or corrective action, and have a supportive healthcare team.
Dr. Ifeoma Uduh, Dr. John Afam