Introduction
Abrupt spikes in brain activity are called seizures, these abrupt spikes in brain activity, are a hallmark of epilepsy, a neurological condition. It is one of the most prevalent neurological disorders in the world, affecting individuals of all ages, genders, and ethnic origins.
Credit: Walker Chiropractic
Better management and care for people with epilepsy can result from educating families and individuals about the condition. What epilepsy is, its causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, available treatments, and ways to support someone who has it will all be covered in this blog article.
What is epilepsy?
A seizure happens when the brain experiences an abrupt, aberrant electrical discharge that interferes with regular brain function. In Nigeria, the prevalence of seizures is about 3.1-37 per 1000 persons. Epilepsy is a chronic noncommunicable disease of the brain that affects around 50 million people worldwide according to WHO.
Unprovoked seizures are a hallmark of epilepsy, a chronic brain illness. Having two or more unprovoked seizures usually results in a diagnosis of epilepsy, however not everyone who has seizures has the condition.
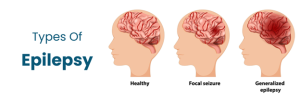
Seizures Types
Credit: MediCover Hospital
Focal Seizures:
One region of the brain experiences focal seizures. They can be separated further into focal onset aware seizures and focal onset impaired seizures.
Generalized Seizures:
These seizures can impair consciousness and affect both sides of the brain. Generalized seizures come in various forms, such as tonic-clonic seizures, the most identifiable kind of seizure (characterized by strong muscular spasms and a loss of consciousness), myoclonic seizures, and absence seizures, which are brief periods of unconsciousness that are frequently confused with daydreaming.
Causes of Epilepsy
Although the precise aetiology of epilepsy is frequently unknown, several factors may play a role in its development:
- Factors related to genetics: Certain forms of epilepsy can run in families because they have a genetic component. Epilepsy risk can also be increased by genetic mutations.
- Stroke: Seizures may result from brain injury caused by a stroke or other vascular catastrophe.
- Brain injury: If brain tissue is scarred as a result of head traumas sustained in trauma, falls, or accidents, epilepsy may develop.
- Infections: Seizures and an increased risk of epilepsy can be caused by illnesses such as meningitis, encephalitis, and other brain infections.
- Developmental disorders: Epilepsy may be linked to conditions such as autism or neurofibromatosis.
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Recurrent seizures are the main sign of epilepsy. However, depending on the person and the type of seizure, symptoms might differ significantly. Typical signs and symptoms include:
- Aura: Before having a seizure, some people may have an aura, which is characterized by peculiar feelings or smells.
- Convulsions: Abrupt, uncontrollable jerking or shaking.
- Loss of awareness
- Confusion
Treatment of Seizures
Though epilepsy has no cure, various treatments help manage seizures. Common options include antiepileptic medications, lifestyle adjustments like sufficient sleep and avoiding triggers, and a balanced diet. In cases where medication is ineffective, surgery or Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) may be an option.
Living With Epilepsy
Although having epilepsy can be difficult, people can lead happy, productive lives if they receive the right care and support. Being aware through education, having psychological support, and frequent follow-ups can help you and your loved ones better manage epilepsy and other disorders.
- Awareness and education: You and their families can make well-informed decisions on lifestyle and treatment if you have a thorough understanding of epilepsy and its effects.
- Explaining illness with others: Explain the illness to friends, family, and coworkers, along with what to do during a seizure.
- Support networks: For people with epilepsy and their families, connect with organizations or support groups offering resources and emotional support.
- Frequent follow-ups: Regular meetings with medical professionals guarantee that the problem is managed effectively.
Conclusion
People of all ages and colours suffer from a complicated neurological condition known as epilepsy. WellaHealth Technologies remains committed to educating and discussing chronic health conditions like Epilepsy to aid in understanding and dismantling myths surrounding it.
In addition, at Wellahealth, we offer affordable and accessible healthcare plans that cover chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes. Contact us to learn more about these medical services.
Article written by Dr. Ifeoma M. Uduh (BDS)
Edited by Dr. John Afam-Osemene (MBBS, DA)