Introduction
Cholesterol is a waxy material necessary for the synthesis of hormones and the development of healthy cells. However, excessive cholesterol can be extremely harmful to your health, especially to your heart and blood vessels. High cholesterol doesn’t show any symptoms until it causes a serious health problem, many people in Nigeria and throughout the world suffer from it without ever realizing it.
Credit: Florida Heart
Our goal is to help you control problems like high cholesterol before they become harmful by offering easily accessible and reasonably priced healthcare solutions.
This article covers what cholesterol is, how it impacts your health, and how to control your cholesterol.
What is Cholesterol?
The liver produces the fatty material known as cholesterol, it produces just enough for your bodily needs. Cholesterol is present in some foods, and although some cholesterol is necessary for your body to function correctly, too much of it can cause issues, in excess, it can be detrimental. To keep the heart healthy, the two forms of cholesterol must be in a healthy balance.
There are two ways that cholesterol moves through the bloodstream namely LDL and HDL:
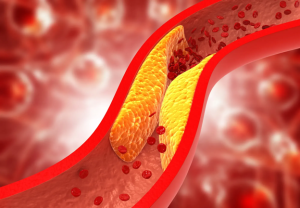
LDL, or low-density lipoprotein: LDL, sometimes referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can accumulate and form plaque on the artery walls. This plaque narrows and hardens the arteries over time (atherosclerosis), limiting blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the major cause of many cardiovascular issues.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Often referred to as “good” cholesterol, HDL assists in removing extra cholesterol from the bloodstream and returning it to the liver for processing and eventual excretion. Your risk of heart disease can be decreased by having higher HDL levels.
Causes For Elevated Cholesterol

Credit: Fidel Perez
Although genetics and other medical issues can also contribute to high cholesterol, lifestyle choices are frequently the cause. Typical causes include the following:
- Age and Gender: People’s cholesterol tends to increase with age. While women’s cholesterol levels tend to rise after menopause, men are more likely to have high cholesterol earlier in life.
- Genetics: Regardless of lifestyle decisions, some people inherit illnesses such as familial hypercholesterolaemia, which results in elevated cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Obesity is linked to decreased HDL and higher LDL cholesterol levels. Higher cholesterol is specifically associated with fat around the belly.
- Poor Diet: LDL cholesterol levels can rise as a result of diets heavy in cholesterol, trans fats, and saturated fats. Common offenders include foods like red meat, processed snacks, and full-fat dairy items.
- Absence of Physical Activity: While inactivity can raise levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides (another form of blood fat), regular exercise helps raise HDL cholesterol.
- Smoking: Smoke from cigarettes weakens the walls of your blood vessels, which facilitates the accumulation of cholesterol. Additionally, smoking reduces HDL cholesterol.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism can affect cholesterol levels.
Health Risks From High Cholesterol
Serious health issues can result from excessive cholesterol, especially high levels of LDL cholesterol. The following are some of the main dangers linked to high cholesterol:
● Heart Conditions
The effects of excessive cholesterol on heart health are among its most harmful effects. Overproduction of LDL cholesterol causes plaques to form in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and preventing oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart. This may result in Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and a heart attack.
● Stroke
The arteries supplying blood to the brain may constrict as a result of high cholesterol. An ischaemic stroke may occur if a blood clot forms or one of these arteries becomes blocked. Strokes are medical emergencies that need to be treated right away to prevent more brain damage, just like heart attacks.
● PAD, or peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease can result from plaque accumulation in the arteries supplying blood to the extremities, especially the legs. Pain, numbness, and an elevated risk of infection in the limbs are all possible outcomes of PAD. In extreme situations, gangrene and amputation may result.
● Elevated blood pressure
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are frequently linked. Plaque accumulation narrows arteries, making it harder for blood to pass through and raising blood vessel pressure. This can eventually result in hypertension, or high blood pressure, which puts additional strain on the heart and raises the risk of stroke and heart disease.
● Kidney Disease
The kidneys depend on functioning blood arteries. Excessive cholesterol can harm the kidneys’ blood arteries, resulting in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and decreased kidney function.
Ways to Avoid and Control Elevated Cholesterol
The good news is that lifestyle modifications, routine exams, and medication when needed can help prevent and manage high cholesterol. You can manage your cholesterol levels in the following ways:
- Consume a heart-healthy diet: Your diet has a big impact on controlling your cholesterol levels. Important nutritional advice: Cut down on saturated fats because saturated fats raise LDL cholesterol, and cut back on meals like red meat, butter, and full-fat dairy products. Getting rid of trans fats which are in baked products and fried foods, might decrease HDL cholesterol while increasing LDL. Add healthy fats to your meals, which are present in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, and can be used to replace saturated fats. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are very good for the heart.
- Engage in regular exercise: Exercise raises HDL cholesterol and lowers LDL cholesterol. On most days of the week, try to get in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as swimming, cycling, or brisk walking. Frequent exercise can lower cholesterol since it aids with weight management.
- Quit smoking: Giving up smoking can lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other major illnesses while also improving your HDL cholesterol. If necessary, get help from counselling, nicotine replacement treatment, or prescription drugs.
- Restrict your alcohol use: While excessive alcohol use can result in heart failure, high blood pressure, and other health problems, moderate alcohol use may raise HDL cholesterol.
- Get screened for high cholesterol frequently: For early detection, routine testing is crucial because elevated cholesterol frequently shows no symptoms. A straightforward blood test known as a lipid profile can assess your cholesterol levels and assist your physician in determining the best course of action for you.
Conclusion
Heart disease, stroke, and other potentially fatal illnesses can be brought on by high cholesterol, a quiet but dangerous health concern. However, you can control your cholesterol and lower your risk of problems by adopting the proper lifestyle choices and scheduling routine medical examinations.
We remain at the forefront of empowering you to take charge of your health. Our reasonably priced health plans guarantee that you will have the resources and assistance required to monitor your cholesterol levels and maintain the health of your heart.
Contact us today to learn how affordable and accessible health plans can help you and your family remain healthy!