Introduction
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are a critical public health issue affecting many Nigerians but due to a lack of knowledge and awareness, they continue to suffer in silence. Additionally, due to the socio-religious stigma attached to diseases such as STIs, many people remain silent and the silence worsens their case making them prone to complications from sexually transmitted diseases like infertility and cancer.

Source: SIDC
WellaHealth Technologies understands the Nigerian clime, so this article will educate you about STIs and how we can help you with your condition and overall health. Wellahealth provides affordable, convenient, and accessible healthcare for all Nigerians. Our plans start at #800/month which affords you a teleconsultation with seasoned doctors, and laboratory tests for common illnesses and infections. To learn more and subscribe to any of our plans visit our website- here.
STIs: What Are They?
Infections known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse, or other forms of sexual contact. STIs can affect all ages and all genders.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are transmitted by sexual contact, including anal, oral, and vaginal sex, and sharing infected sexual toys. STIs may be brought on by fungi, viruses, bacteria, or parasites. In some cases, they can also be spread through non-sexual means, such as from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding, and through blood transfusions or shared needles.
While some STIs are easily treated, if they are not, some can result in major health issues. Among the prevalent STIs are: Chlamydia, Syphilis, Gonorrhoea, HIV, or the human immunodeficiency virus, Genital Warts from Human papillomavirus (HPV), HSV, or Herpes Simplex Virus, viral hepatitis (HEP-B), and trichomonas infection.
Common STI Types
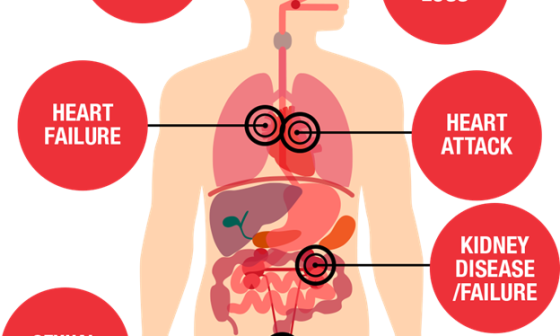
- Chlamydia: Chlamydia is a bacteria infection that frequently exhibits no symptoms, but in women, it can induce pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can result in infertility.
- Gonorrhea: If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and spread to the bloodstream causing varying symptoms like first-trimester abortion, infertility in men and women, and complications in babies born to infected mothers. It is a bacterial infection
- Syphilis: A bacterial infection that although the disease’s early signs may be mild, if untreated, can harm the neurological system and internal organs.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This virus comes in a variety of types, some of which can lead to cervical cancer and genital warts.
- HIV: The virus that causes AIDS, a long-term immune-system-weakening illness.
- Hep-B: Viral Hepatitis type B (Hep B ) is spread through bodily fluids like blood or semen and can lead to chronic liver disease and liver cancer. Vaccination is crucial for prevention.
Signs and Symptoms of STIs
STI symptoms might differ greatly according to the type of infection. While some people may exhibit obvious symptoms, others may be asymptomatic—that is, not exhibit any infection-related symptoms at all. However, typical signs and symptoms include:
- Painful urination,
- Frequent urination,
- burning feeling during urination,
- abnormal discharge coming from the vagina or penis,
- bumps, warts, or sores on the vaginal, penis, or anal region,
- itchiness or irritation around the genital area,
- discomfort during sexual activity,
- painful/ difficult sexual intercourse,
- vaginal bleeding (abnormal bleeding not from periods),
- general body symptoms like night sweats, unintended weight loss, skin rash, aches, chills, jaundice (yellowing of the eyes), and
- enlarged lymph nodes
The most crucial thing to do is to consult a doctor or other healthcare provider right once you get any STI symptoms. Serious health complications can be avoided by receiving early diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors for Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)
- Engaging in sexual activity puts you at risk of contracting an STD (sexually transmitted infection).
- Sharing private objects like needles that contain your blood can also result in an STI.
- tattoos without regulations.
- body piercings from unregulated places.
- Substance abuse- sharing needles is common
How are sexually transmitted infections diagnosed?
STIs are diagnosed after a physical examination and testing done by your doctor. After a positive STI diagnosis, you must inform your sexual partner(s), to enable them to get tested. Telling your partners is important and may be a vulnerable process but need it to help their health and prevent the spread of the infection.
STI testing may involve a urine test, a cheek swab, a blood test, a fluid sample from a skin sore, or a discharge or cell sample from your body (usually the throat, vagina, urethra, cervix, penis, or anus).
The majority of STI testing is painless, though some tests may cause a small pinch or sting when a swab comes into contact with a sore.
Management of STIs
In many cases, STIs can be cured by following the treatment regimen while for most viral STIs can be managed with drugs. While the infection may not be cured, the medications can lessen your symptoms, reduce your likelihood of spreading the infection, and maintain you in good health.
Treatment for STIs could include taking oral or injection medications like Antibiotics, Antiprotozoals, and Antivirals.
STI Prevention (ABC of infection)

Source: CDC
To stop STIs from spreading, prevention is essential. Here are a few successful tips:
- A(Abstinence): The best defence against STIs is to never engage in sexual activity.
- B (Be faithful): Maintaining a mutually monogamous relationship for an extended period with a partner who has undergone testing and is confirmed to be infection-free.
- C (Condoms): The risk of getting and spreading STIs can be considerably decreased by using condoms correctly and consistently.
- Immunization: There are vaccines available against a few STIs, including hepatitis B and HPV.
- Education: Get knowledgeable about STIs and your health. You can better protect yourself and your relationships the more informed you are. Find out what STI symptoms and indicators are, and see a doctor as soon as possible if you experience any symptoms.
- Frequent screenings: Early infection detection and prevention of spread to others can be achieved through routine STI testing.
Conclusion
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) impact millions of people annually and are a major global public health concern. Even with their widespread occurrence, these illnesses are nevertheless the subject of a lot of stigma and false information.
With a focus on common types, symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and treatment, this article seeks to give readers a compassionate and educational overview of sexually transmitted infections.
Dr.Ifeoma M. Uduh, Dr. John Afam-Osemene




1 comment